In industrial automation, network reliability is critical to ensuring uninterrupted operations. Redundancy ring protocols provide fault tolerance by enabling fast recovery from network failures, minimizing downtime in industrial Ethernet networks.
This article explores how redundancy ring protocols work, their key features, and a list of popular protocols, including proprietary solutions from leading vendors such as Moxa, Hirschmann, and Cisco.
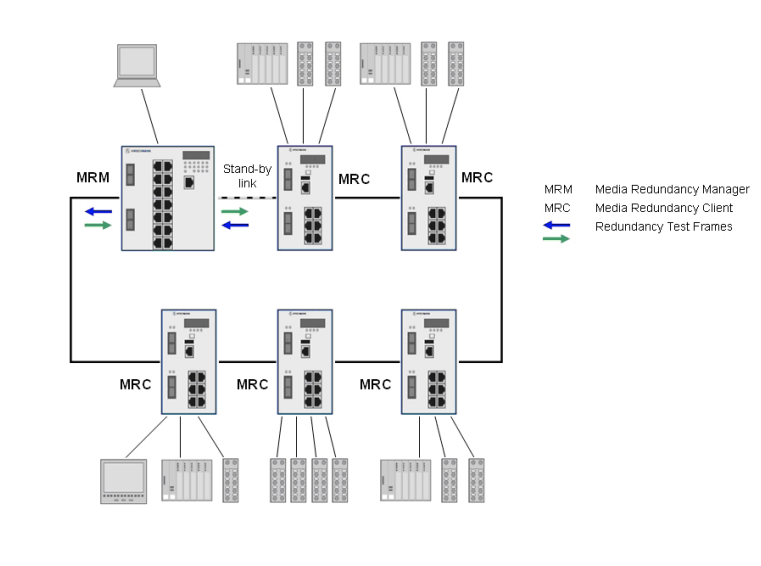
How Redundancy Ring Protocols Work
Redundancy ring protocols establish a ring topology where network switches and devices are connected in a loop. These protocols ensure:
- Continuous Network Operation: If a failure occurs (e.g., a cable break or switch failure), the protocol re-routes traffic via an alternate path.
- Fast Network Recovery: Most protocols offer recovery times below 50 ms, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Efficient Traffic Management: Protocols prevent broadcast storms by blocking redundant paths until needed.
Key Working Principles
- Primary and Backup Paths: Normally, one segment in the ring is blocked to prevent looping.
- Fault Detection: The protocol continuously monitors the network for link failures.
- Automatic Reconfiguration: If a failure is detected, the blocked path is quickly activated to restore connectivity.
- Recovery Time: Varies by protocol but typically ranges from <10 ms to 50 ms.
Features of Redundancy Ring Protocols
- Fast Convergence: Quick recovery from link failures to maintain network uptime.
- Scalability: Supports multiple switches and large networks.
- Load Balancing: Some protocols distribute traffic across redundant links.
- Interoperability: Many protocols follow open standards, while others are vendor-specific.
- Support for Industrial Applications: Designed for SCADA, PLC, and factory automation environments.
Popular Redundancy Ring Protocols
1. Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP – IEEE 802.1D-2004)
- Standardized by IEEE for Ethernet networks.
- Provides network redundancy with recovery times of 1-3 seconds.
- Not as fast as proprietary industrial ring protocols.
2. Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP – IEC 62439-2)
- Commonly used in PROFINET networks.
- Offers recovery times of <10 ms for fast fault recovery.
- Works with industrial Ethernet switches and PLCs.
3. Device Level Ring (DLR – ODVA Standard)
- Developed for EtherNet/IP networks.
- Recovery time of <3 ms.
- Typically used in Rockwell Automation / Allen-Bradley systems.
Proprietary Redundancy Ring Protocols by Major Vendors
Many industrial network equipment manufacturers offer proprietary redundancy solutions with enhanced performance and features.
1. Moxa – Turbo Ring
- Offers a recovery time of <20 ms with up to 250 switches.
- Designed for factory automation, transportation, and power substations.
- Supports multiple rings in a single network.
2. Hirschmann (Belden) – HIPER Ring
- Recovery time of <10 ms.
- Supports multiple rings and redundant paths.
- Used in power utilities, oil & gas, and transportation networks.
3. Advantech – X-Ring
- Provides recovery time of <10 ms.
- Supports Auto-Recovery and Dual-Ring topology.
- Suitable for IIoT and smart factory applications.
4. Siemens – High-Speed Redundancy (HSR) & Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP)
- HSR: Provides zero recovery time by duplicating packets on both paths.
- PRP: Ensures redundancy using two independent networks.
- Ideal for mission-critical applications such as power grids.
5. Cisco – REP (Resilient Ethernet Protocol)
- Cisco’s proprietary ring redundancy protocol.
- Offers faster recovery than RSTP while maintaining Ethernet compliance.
- Used in industrial automation and large-scale enterprise networks.
6. Red Lion – N-Ring
- Features recovery time of <30 ms.
- Designed for industrial Ethernet switches.
- Ensures self-healing network topology.
Comparison of Redundancy Ring Protocols
| Protocol | Recovery Time | Use Case | Standard/Open |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSTP (IEEE 802.1D) | 1-3 sec | General industrial networks | Open (IEEE) |
| MRP (IEC 62439-2) | <10 ms | PROFINET networks | Open (IEC) |
| DLR (ODVA) | <3 ms | EtherNet/IP devices | Open (ODVA) |
| Turbo Ring (Moxa) | <20 ms | Factory automation, transport | Proprietary |
| HIPER Ring (Hirschmann) | <10 ms | Power, oil & gas, transport | Proprietary |
| X-Ring (Advantech) | <10 ms | Smart factory, IIoT | Proprietary |
| HSR/PRP (Siemens) | 0 ms (HSR) | Power grids, mission-critical | Open (IEC) |
| REP (Cisco) | Fast recovery | Industrial automation | Proprietary |
| N-Ring (Red Lion) | <30 ms | Industrial Ethernet switches | Proprietary |
Conclusion
Redundancy ring protocols are essential for ensuring high availability and fault tolerance in industrial networks. While standard solutions like RSTP, MRP, and DLR offer broad compatibility, proprietary protocols like Turbo Ring, HIPER Ring, and X-Ring provide optimized performance for specific industrial applications.
Choosing the right protocol depends on factors such as recovery time, network size, interoperability, and industry requirements. As industrial networks evolve, high-speed redundancy solutions like HSR and PRP will play an increasingly vital role in mission-critical applications.